Hit-and-Run Crashes: Prevalence, Contributing Factors and Countermeasures
Hit-and-run crashes and fatalities rates have been increasing at an alarming rate.
April 2018
Suggested Citation
For media inquiries, contact:
Tamra Johnson
202-942-2079
TRJohnson@national.aaa.com
Abstract
Hit-and-run collisions are those in which at least one person involved in a crash flees the scene before offering any (or sufficient) information or aid to the other involved person(s) or fails to properly report the crash. Hit-and-run crashes contribute to the suffering and social and economic burdens typical of injury crashes but also can increase the severity of outcomes given delays in or the complete absence of medical attention for the victims. Moreover, hit-and-run violations– which are criminal offenses–can create additional burdens for law enforcement and for families looking for remediation and medical and insurance support.
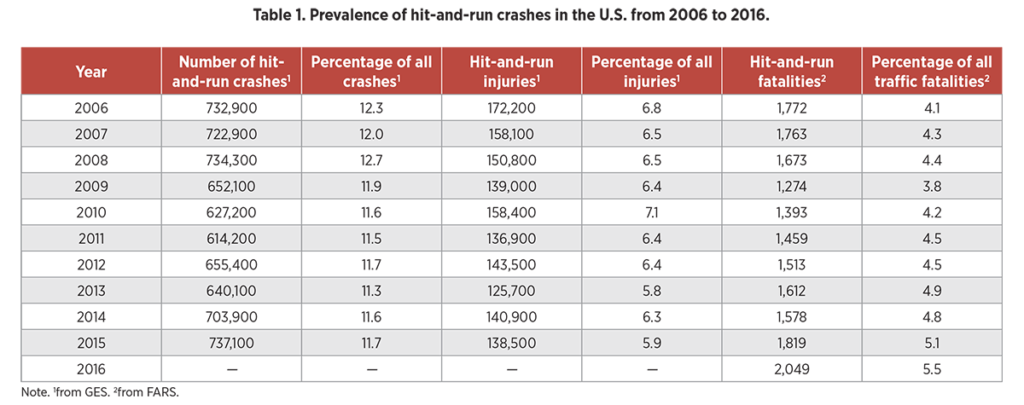
The current analysis found that both the rates of hit-and-run crashes and fatalities are increasing. There were an estimated 737,100 hit-and-run crashes in 2015 (NHTSA, 2016). This translates to a hit-and-run crash happening somewhere in the U.S. every 43 seconds. The 2,049 fatalities that resulted from hit-and-run crashes in 2016 were the highest number ever recorded (NHTSA, 2017).
In addition to providing updated statistics concerning hit-and-run crashes, this brief provides a review of some of the scientific literature on environmental, vehicle and individual factors that are associated with this crash type as well as models and theories that speculate on the etiology of these crashes. Additionally, existing countermeasures that have been implemented in various states are reviewed. Lastly, areas of future research and data needs are described.
Methodology
Data from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) Fatality Analysis Reporting System (FARS) were used to quantify fatal crashes and deaths.
Results
In 2016, there were 1,980 fatal hit-and-run crashes resulting in 2,049 fatalities.
Suggested Citation
For media inquiries, contact:
Tamra Johnson
202-942-2079
TRJohnson@national.aaa.com